Autoclave Safety is vital in laboratories, hospitals, veterinary clinics, and research facilities. These powerful machines sterilize equipment and biohazard waste using high-pressure steam.
While they are indispensable for infection control, improper use can lead to severe burns, explosions, and equipment failure.
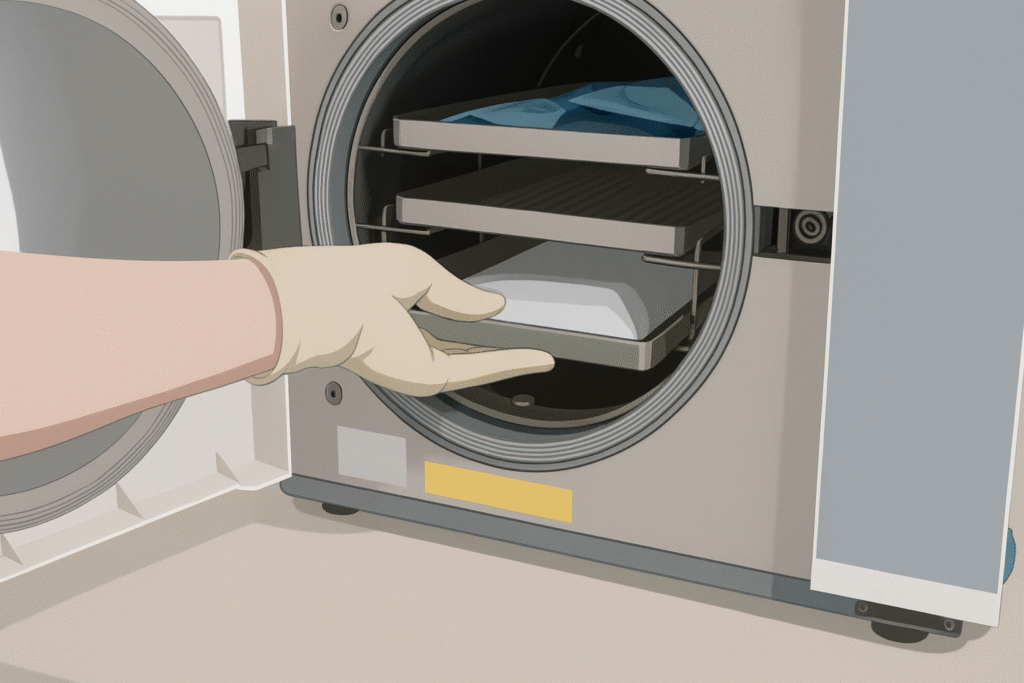
Workers must follow strict procedures to operate autoclaves safely. This article covers essential safety steps, potential hazards, and risk mitigation strategies to ensure a secure working environment.
What is an Autoclave?
An autoclave is a pressure chamber used to sterilize instruments, glassware, biological waste, and other materials by applying saturated steam at high temperature (usually 121°C to 134°C) for a set time.
Autoclaves are widely used in:
- Clinical labs and hospitals for surgical tool sterilization
- Microbiology labs for sterilizing cultures and media
- Animal care facilities for sanitizing cages and instruments
Because they operate under extreme heat and pressure, they pose serious risks without proper care.
Common Risks Associated with Autoclaves
Autoclave-related injuries and incidents often stem from:

- Steam Burns: Occur when users open the chamber prematurely or contact hot surfaces.
- Pressure-Related Explosions: Caused by over-pressurization or faulty gaskets/seals.
- Handling Hot Loads: Burns from mishandling sterilized items without PPE.
- Shattered Glassware: Due to incorrect loading or incompatible materials.
- Inhalation of Toxic Vapors: Especially when sterilizing chemical waste or biohazards.
Each of these can result in hospitalization, property damage, or workplace shutdowns.
Autoclave Safety: Operating Procedures to Follow
1. Training and Authorization
Only trained and authorized personnel should operate autoclaves. Workers must understand:
- How the autoclave works
- Material compatibility
- Cycle selection
- Emergency procedures
Annual refresher training is recommended.
2. Pre-Use Inspection
Before using the autoclave, check for:
- Cracked gaskets or seals
- Clogged drain lines
- Leaking steam valves
- Damaged trays or shelves
Report issues immediately and avoid use until maintenance is completed.
3. Load the Autoclave Correctly
Improper loading can lead to incomplete sterilization or equipment damage. Best practices include:
- Leaving space between items for steam circulation
- Placing wrapped instruments upright
- Avoiding overloaded trays
- Using only autoclave-safe containers (e.g., polypropylene, borosilicate glass)
Do not place tightly sealed containers or volatile substances inside unless permitted.
4. PPE Requirements
Operators must wear:
- Heat-resistant gloves
- Lab coat or apron
- Face shield or safety goggles
- Closed-toe, non-slip footwear
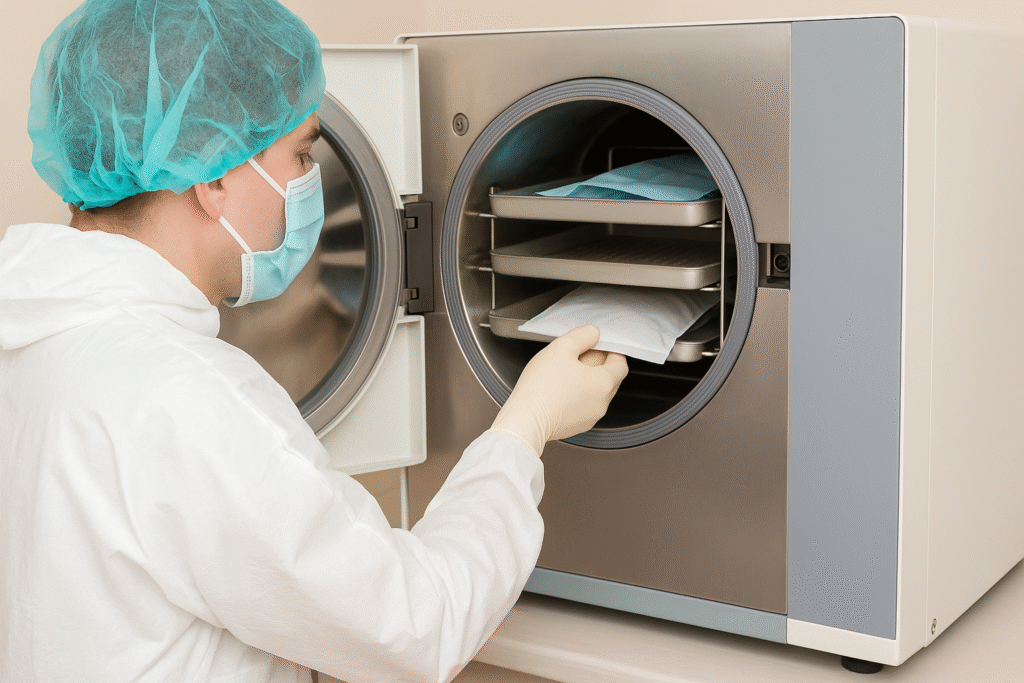

This protects against scalding steam and hot surfaces.
👉 Browse PPE options at SafetyProductSupply.com (DoFollow link)
5. Safe Operating Procedures
- Choose the correct sterilization cycle for the load type.
- Always start a cycle with the chamber door fully latched.
- Never open the door mid-cycle or while pressure is above zero.
- Allow items to cool before removal.
- Use tongs or heat-proof trays when handling hot materials.
Some institutions provide cooldown indicators or timers to ensure safety.
6. Waste Autoclaving Procedures
If autoclaving biohazard or chemical waste:
- Use labeled biohazard bags with built-in steam vents.
- Place bags in autoclave-safe secondary containers.
- Avoid autoclaving materials like bleach or reactive chemicals.
- Allow steam to escape gradually before opening the door.
Maintenance and Emergency Planning
Routine maintenance is crucial for long-term autoclave safety:
- Perform monthly seal checks and gasket replacements.
- Clean drain lines and trays weekly.
- Schedule annual inspections by certified technicians.
Also, display an Emergency Contact Sheet with:
- First aid response steps for burns
- Spill containment plans
- Maintenance personnel details
- Fire extinguisher and eye wash station locations

Real Case: Autoclave Incident
A research technician suffered second-degree burns after opening a pressurized autoclave that had not depressurized properly. The root cause: bypassing the cooldown wait period and lack of visible pressure indicator.
Incidents like this underscore the importance of Autoclave Safety practices and clear operator guidelines.
Autoclave Safety Protocol
| Task | Done? |
|---|---|
| Performed pre-use equipment check | ✅ |
| Wore required PPE | ✅ |
| Verified material compatibility | ✅ |
| Selected proper cycle | ✅ |
| Waited for pressure to drop | ✅ |
| Used heat-resistant handling tools | ✅ |
Final Thoughts on Autoclave Safety
Autoclave Safety must never be taken lightly. This powerful equipment is an essential part of workplace hygiene, but it’s also one of the most dangerous if handled improperly.
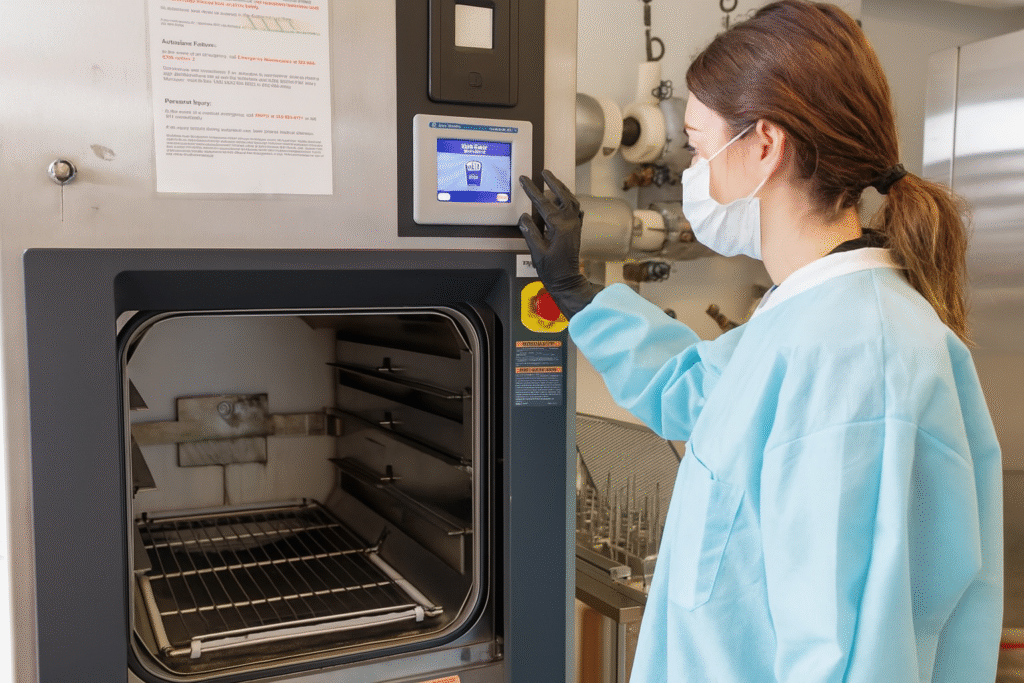

By following correct operating procedures, wearing PPE, conducting inspections, and receiving regular training, organizations can prevent burns, explosions, and chemical exposures.
Whether you manage a university lab or a hospital sterilization unit, promoting Autoclave Safety should be a top priority.

No comments yet