Safety for HVAC Technicians
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) technicians perform essential tasks that ensure our homes, offices, and industries remain comfortable and functional.
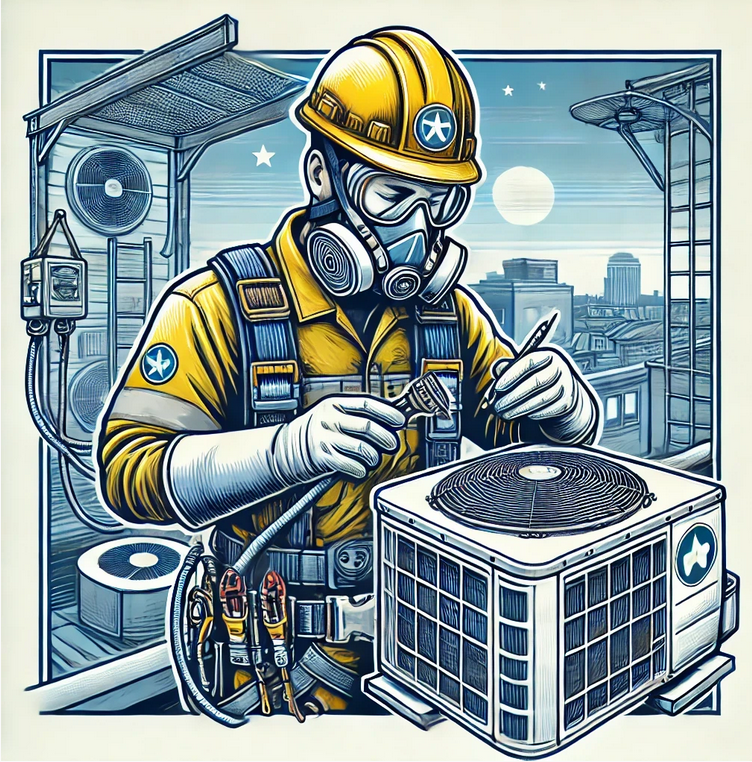

However, their work often involves exposure to various hazards, such as electrical systems, heavy machinery, and hazardous materials. Prioritizing occupational safety is critical to protect HVAC technicians from injuries and illnesses while maintaining efficient operations.
This article explores the key occupational safety challenges faced by HVAC technicians, best practices for mitigating risks, and resources for ensuring compliance with safety standards.
1. Common Hazards in HVAC Work
HVAC technicians encounter a range of hazards during their daily tasks. Understanding these risks is the first step in creating safer work environments.
1.1. Electrical Hazards
- Exposure to live wires or faulty electrical systems can result in shocks, burns, or electrocution.
- Poor grounding or improper use of electrical tools increases risks.
1.2. Chemical Exposure
- Refrigerants, cleaning agents, and other chemicals used in HVAC work can cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, or more severe health conditions.
- Leaks or spills may expose technicians to harmful substances like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
1.3. Physical Strain
- Lifting heavy equipment, awkward postures, and repetitive movements contribute to musculoskeletal injuries.
- Working in confined spaces or at heights poses additional risks.
1.4. Heat and Cold Stress
- Technicians often work in extreme temperatures, leading to heat exhaustion, heatstroke, or frostbite.
1.5. Falls and Injuries
- Slips, trips, and falls are common, particularly when working on rooftops or ladders.
- Improper use of tools or equipment can result in cuts, fractures, or other injuries.
2. Best Practices for HVAC Technician Safety
Employers and technicians can adopt practical measures to minimize risks and create a safer work environment.
2.1. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Required PPE for HVAC Work:
- Insulated gloves and tools for electrical safety.
- Safety goggles to protect against debris and chemical splashes.
- Steel-toe boots for foot protection.
- Respirators for environments with poor air quality or chemical exposure.
2.2. Adherence to Safe Work Practices
- Always de-energize electrical equipment before repairs.
- Use proper lifting techniques to prevent back injuries.
- Follow manufacturers’ guidelines for tools and equipment.
2.3. Regular Training and Certification
- Provide training on handling hazardous materials and emergency procedures.
- Ensure technicians have up-to-date certifications for refrigerants and electrical work.
2.4. Maintaining a Safe Work Environment
- Keep work areas clean and organized to prevent slips and trips.
- Use fall protection systems when working at heights.
3. Regulatory Standards for HVAC Safety
Compliance with safety regulations is essential to protect technicians and avoid legal liabilities. Key regulations include:
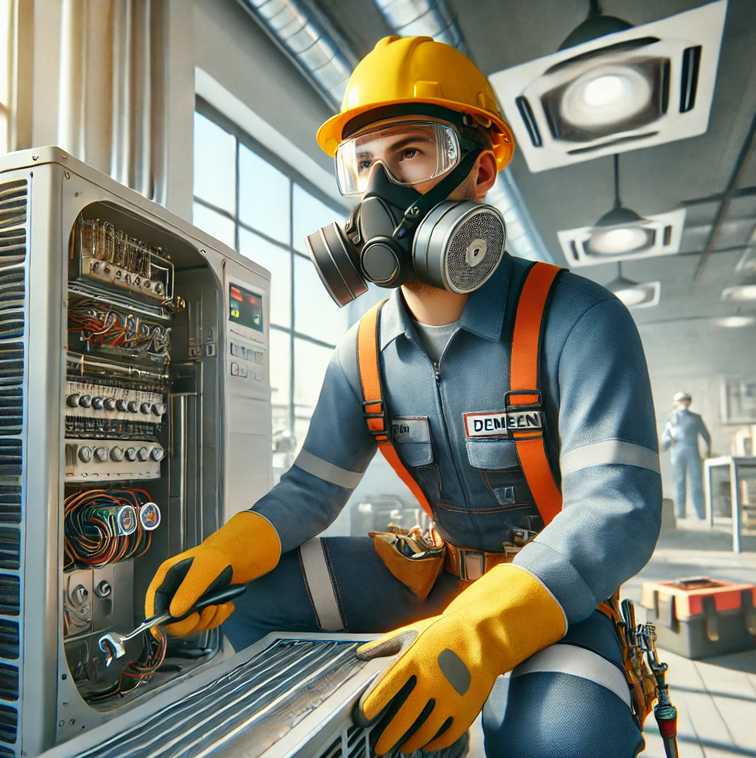

- OSHA Standards:
- General Industry Standard (29 CFR 1910): Addresses hazards like electrical safety and chemical exposure.
- Construction Standard (29 CFR 1926): Applies to HVAC work in construction settings.
- EPA Requirements:
- Certification for handling refrigerants under Section 608 of the Clean Air Act.
- Local Codes and Standards:
- Ensure adherence to regional building codes and safety guidelines.
Explore more at OSHA’s HVAC Safety Resources and EPA’s Refrigerant Management Program.
4. The Role of Employers in HVAC Safety
Employers play a critical role in ensuring the safety of HVAC technicians by:
- Providing Safety Equipment: Supply appropriate PPE and tools.
- Conducting Risk Assessments: Identify potential hazards and implement mitigation strategies.
- Offering Ongoing Training: Regularly update technicians on safety procedures and industry advancements.
- Encouraging Reporting: Foster a culture where technicians feel comfortable reporting hazards or near misses.
5. Tips for HVAC Technicians to Stay Safe
Technicians can take proactive steps to protect themselves on the job:
- Perform Pre-Job Inspections: Assess the work area and equipment before starting.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, especially when working in hot environments.
- Avoid Shortcuts: Always follow proper procedures, even when pressed for time.
- Communicate: Notify team members about potential hazards or unexpected conditions.
6. The Future of HVAC Safety
Emerging technologies and innovations are transforming HVAC safety:
- Smart PPE: Wearable devices that monitor heat stress, air quality, and vital signs.
- Automation: Tools that reduce manual labor, such as robotic duct cleaners.
- Virtual Training: VR-based training programs that simulate real-world scenarios.
Safety is Non-Negotiable
Occupational safety for HVAC technicians is not just a regulatory requirement but a moral imperative. By understanding the hazards, adhering to best practices, and fostering a culture of safety, employers and technicians can ensure a secure and productive work environment.
With the right training, equipment, and awareness, HVAC professionals can continue to deliver vital services without compromising their health and safety.
For more resources on HVAC safety, visit NIOSH’s Workplace Safety or OSHA’s HVAC Guidelines.Occupational Safety for HVAC Technicians: Protecting Those Who Keep Us Comfortable

No comments yet