In any workplace, the safety and well-being of employees are paramount. One of the most effective ways to protect workers from potential hazards is through the use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
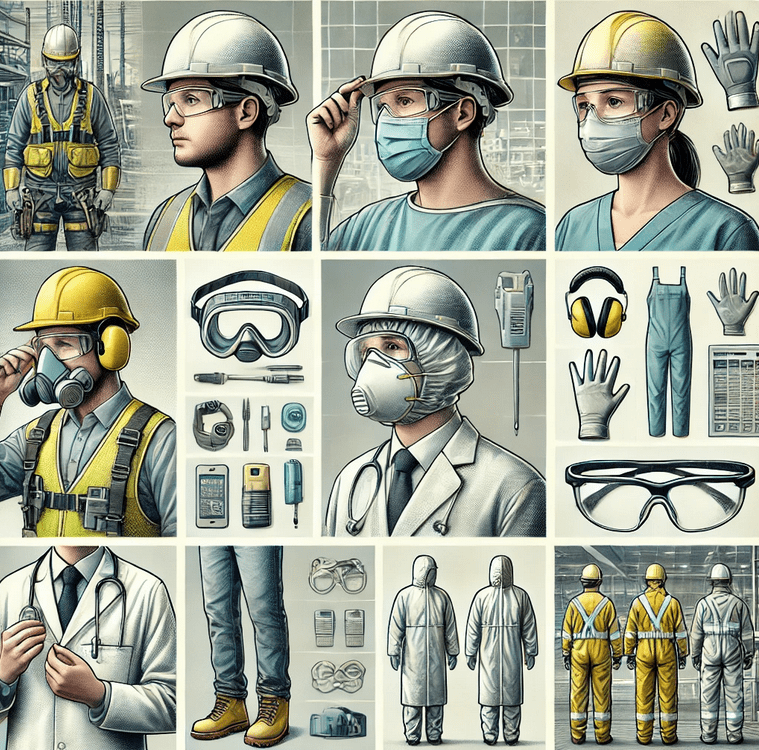
PPE serves as the last line of defense against workplace hazards, minimizing the risk of injury, illness, or death.
This article explores the importance of PPE in Occupational Health and Safety (OHS), the types of PPE available, and the responsibilities of both employers and employees in ensuring its proper use.
The Role of PPE in Occupational Health and Safety
PPE is designed to protect workers from a wide range of hazards, including physical, chemical, biological, and ergonomic risks.
In many industries, such as construction, healthcare, manufacturing, and mining, workers are exposed to dangers that cannot always be eliminated or controlled by engineering or administrative measures. In these cases, PPE becomes essential in providing the necessary protection.
The primary role of PPE is to reduce the risk of injury or illness by creating a barrier between the worker and the hazard. For example, in construction, hard hats protect against falling objects, while gloves and safety boots prevent hand and foot injuries. In healthcare, PPE such as gloves, masks, and gowns protect against exposure to infectious diseases.
Types of PPE
PPE comes in various forms, each designed to protect specific parts of the body or from specific hazards. The most common types of PPE include:
- Head Protection: Helmets, hard hats, and bump caps protect against head injuries from falling objects or collisions.
- Eye and Face Protection: Safety glasses, goggles, face shields, and welding helmets protect the eyes and face from flying debris, chemicals, radiation, or splashes.
- Hearing Protection: Earplugs and earmuffs reduce exposure to harmful noise levels that can cause hearing loss.
- Respiratory Protection: Masks, respirators, and breathing apparatus protect against inhalation of harmful dust, fumes, vapors, or biological agents.
- Hand Protection: Gloves made of various materials protect against cuts, burns, chemical exposure, and electrical hazards.
- Foot Protection: Safety boots and shoes with protective toe caps, puncture-resistant soles, and insulation protect against foot injuries from falling objects, sharp materials, and extreme temperatures.
- Body Protection: Overalls, aprons, and protective suits shield the body from chemicals, heat, and contamination.
- Fall Protection: Harnesses, lanyards, and safety nets prevent falls from heights in industries such as construction and maintenance.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers have a legal and ethical obligation to provide a safe working environment for their employees. This includes ensuring that appropriate PPE is available and used correctly. Key employer responsibilities include:
- Hazard Assessment: Conducting regular assessments to identify potential hazards in the workplace and determining the necessary PPE for each task.
- Provision of PPE: Providing employees with the appropriate PPE at no cost and ensuring it is readily available when needed.
- Training: Offering training on the proper use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE. Employees must understand how to wear PPE correctly and the importance of using it consistently.
- Maintenance and Replacement: Regularly inspecting PPE for signs of wear and tear and replacing it as needed to ensure it remains effective.
Employee Responsibilities
While employers are responsible for providing PPE, employees also have a role to play in ensuring their safety. Employee responsibilities include:
- Proper Use: Wearing PPE correctly and consistently whenever it is required. This includes following the manufacturer’s instructions and any training provided by the employer.
- Inspection: Regularly inspecting PPE before use to ensure it is in good condition. Damaged or defective PPE should be reported immediately and replaced.
- Maintenance: Taking care of PPE by cleaning and storing it properly to prolong its lifespan and effectiveness.
- Reporting Hazards: Reporting any hazards or concerns related to PPE to supervisors or safety personnel.
Conclusion
Personal Protective Equipment is a crucial component of workplace safety, serving as a vital defense against various hazards. However, PPE should not be viewed as a standalone solution but as part of a comprehensive OHS strategy that includes hazard identification, risk assessment, and control measures. By understanding the importance of PPE and fulfilling their respective responsibilities, both employers and employees can contribute to a safer and healthier work environment.
In conclusion, the effective use of PPE can prevent countless injuries and illnesses, ensuring that workers go home safely at the end of each day. As the last line of defense, it is essential that PPE is given the attention and respect it deserves in the workplace.

No comments yet