Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries is a core focus in any industrial or manufacturing environment.
These hazards are not only among the most common causes of serious workplace injuries, but they can also be life-altering—resulting in crushed limbs, amputations, or fatalities.
As machines become faster and more automated, the need for proactive safety strategies becomes more urgent.
This article dives into the key risks, prevention strategies, required training, and equipment that can help create a safer workspace.
- Understanding the Hazards: What Are Entanglement and Pinch Points?
- Common Equipment with Entanglement and Pinch Point Risks
- Key Strategies for Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries
- Real-Life Case Example
- Pinch Point Safety: Quick Checklist for Workers
- Buying Safety Equipment for Entanglement & Pinch Point Prevention
- Final Thoughts on Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries
Understanding the Hazards: What Are Entanglement and Pinch Points?
- Entanglement Injuries occur when loose clothing, jewelry, hair, or PPE gets caught in rotating machine parts such as shafts, gears, pulleys, or conveyors.
- Pinch Point Injuries happen when a person’s body part is caught between two moving parts—or between a moving and a stationary part—resulting in crushing or lacerations.
According to CCOHS, these injuries are prevalent in manufacturing, construction, warehousing, and food processing industries, and most are preventable with proper engineering controls and awareness.
Common Equipment with Entanglement and Pinch Point Risks
| Machine Type | Common Hazards |
|---|---|
| Conveyor Belts | Loose clothing or fingers caught in rollers |
| Mechanical Presses | Hands or arms crushed during operation |
| Rotating Shafts/Gears | Hair and jewelry entanglement |
| Rollers and Mixers | Limb entrapment |
| Lift Tables and Jacks | Pinch points under load mechanisms |
| Doors/Hinges/Drawers | Finger pinching injuries |
These machines often operate silently and quickly, giving workers little time to react if something goes wrong.

Key Strategies for Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries
1. Use Machine Guards and Barriers
All moving parts must be protected by physical guards that prevent access during operation. These include:
- Fixed or interlocking guards
- Two-hand controls
- Emergency stop buttons
- Light curtains or sensors in automated environments
Never remove or bypass machine guards. Doing so violates safety regulations and exposes workers to serious harm.
2. Implement Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures
Before performing maintenance or clearing jams, workers must follow proper LOTO protocols to ensure machines are fully de-energized and cannot be restarted accidentally. This is mandated by OSHA and provincial regulations.
Refer to our article on Safe Use of Compressed Gas Cylinders for more on LOTO applications in various industries.
3. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Supervisors and safety officers should routinely inspect machines to identify new or hidden pinch points and entanglement risks. Add controls as needed and update safe work procedures accordingly.
4. Enforce PPE and Dress Code Compliance
Workers must avoid:
- Loose clothing, hoodie strings, and scarves
- Dangling jewelry or lanyards
- Long untied hair
Use hair nets, wrist guards, close-fitting gloves (where appropriate), and tear-away clothing in high-risk areas.
Visit SafetyProductSupply.com to purchase CSA-compliant gloves, coveralls, and machine-safe PPE.
5. Provide Comprehensive Training

Train all machine operators on:
- Hazard identification
- Emergency stop usage
- Guarding functions
- Recognizing pinch point diagrams
- PPE protocols and dress policies
Refresher training should be provided yearly or when new machines are introduced.
Real-Life Case Example
A worker operating an unguarded conveyor belt reached over to clear debris. Their sleeve was caught, pulling the arm into the rollers.
Had proper guarding and stop-switch training been provided, the injury—and its consequences—could have been avoided.

Incidents like these highlight why Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries isn’t optional—it’s vital.
Pinch Point Safety: Quick Checklist for Workers
| Action | Completed |
|---|---|
| Machine inspected before use | ✅ |
| All guards in place and secure | ✅ |
| No loose clothing, jewelry, or untied hair | ✅ |
| Emergency stop buttons functional | ✅ |
| LOTO applied before service/maintenance | ✅ |
| Awareness of moving parts and crush zones | ✅ |
Buying Safety Equipment for Entanglement & Pinch Point Prevention
To ensure your workplace is equipped with the right tools and safety wear, shop certified PPE and guarding tools from:
👉 SafetyProductSupply.com – Find safety gloves, signage, hazard tags, protective clothing, and more (DoFollow).
Final Thoughts on Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries
Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries requires commitment from both employers and workers. With proper training, enforced PPE rules, effective guarding, and smart operational design, workplaces can significantly reduce injury risks.
If your machines move, rotate, or lift—someone’s life could change in an instant. Don’t wait for an incident to force change. Be proactive. Train, guard, inspect, and protect. Because every machine can be dangerous—but every injury can be preventable.
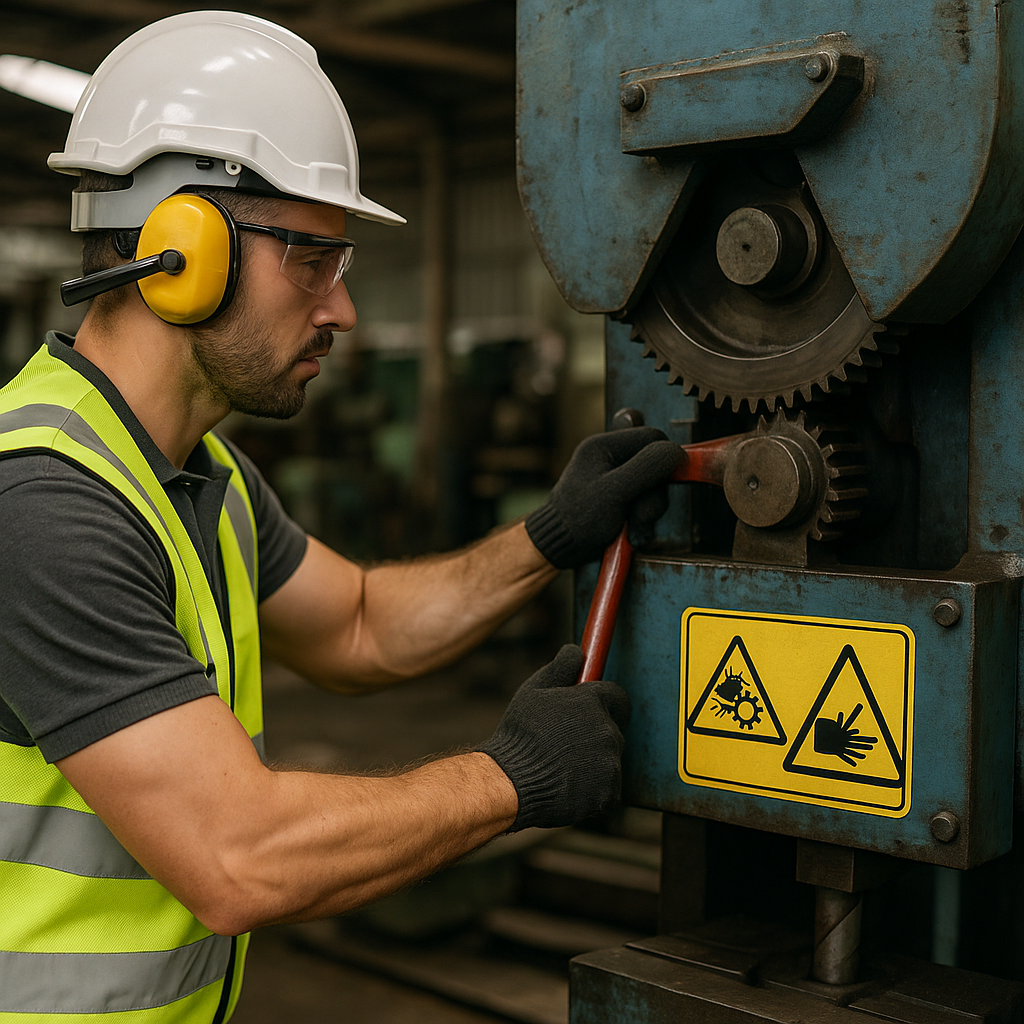

Focus Keyword Recap: Preventing Machine Entanglement and Pinch Point Injuries is essential in every work environment involving moving parts or automated systems.
Use this guide to build a safer workspace and reinforce safety culture from the ground up.

No comments yet