Introduction
Auto mechanics play an essential role in maintaining and repairing vehicles, ensuring their safety and efficiency. However, the profession involves exposure to numerous hazards, including physical, chemical, and ergonomic risks.
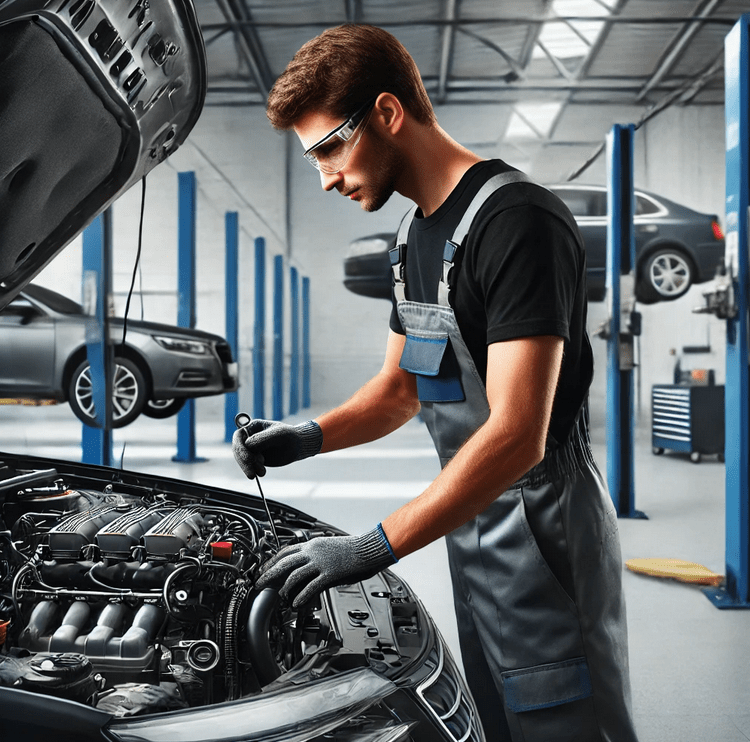
Implementing health and safety measures in the workplace not only protects mechanics but also enhances productivity and job satisfaction.
This guide explores key Occupational Health and Safety (OH&S) practices for auto mechanics.
1. Physical Hazards
Working with heavy machinery, tools, and vehicles exposes auto mechanics to potential physical injuries, including cuts, bruises, burns, and fractures.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Use Protective Equipment: Wear gloves, safety goggles, steel-toed boots, and overalls to minimize physical injuries.
- Tool Safety: Inspect tools and equipment regularly to ensure they are in good working condition.
- Vehicle Lifting: Use vehicle lifts or jacks that meet safety standards, and always secure vehicles with jack stands before working underneath.
- Workspace Organization: Keep the workspace tidy to prevent slips, trips, and falls.
2. Chemical Hazards
Mechanics handle various chemicals, including lubricants, solvents, and fuel, which can cause skin irritation, respiratory issues, or long-term health effects.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS): Familiarize yourself with the MSDS for each chemical used and follow the recommended safety precautions.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure the workshop is well-ventilated to reduce exposure to fumes.
- Use PPE: Wear gloves and masks when handling hazardous substances.
- Chemical Storage: Store chemicals in labeled containers and in designated storage areas away from heat or ignition sources.
3. Ergonomic Risks
Auto mechanics often work in awkward positions, such as bending, twisting, or reaching, which can lead to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs).
Health and Safety Tips:
- Adjustable Equipment: Use adjustable creepers, stools, and lifts to maintain comfortable working positions.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Lift heavy objects with your legs, not your back, to avoid strain.
- Task Rotation: Alternate between tasks to reduce repetitive motion injuries.
- Stretching Exercises: Incorporate regular stretching to improve flexibility and reduce tension.
4. Fire and Explosion Hazards
Auto mechanics work with flammable liquids like gasoline and oil, increasing the risk of fire and explosions.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Fire Extinguishers: Keep fire extinguishers easily accessible and ensure they are inspected regularly.
- No Smoking Policy: Enforce a strict no-smoking policy in areas where flammable materials are present.
- Spill Management: Clean up fuel or oil spills immediately to prevent fire risks.
- Electrical Safety: Avoid using damaged electrical cords or equipment near flammable substances.
5. Noise and Hearing Protection
Loud machinery and tools can cause hearing damage over time if adequate precautions are not taken.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Hearing Protection: Wear earplugs or earmuffs when operating noisy equipment.
- Maintenance: Keep machinery well-maintained to reduce noise levels.
- Noise Monitoring: Regularly monitor noise levels in the workshop and address any excessive noise issues.
6. Respiratory Risks
Exposure to dust, exhaust fumes, and chemical vapors can lead to respiratory issues over time.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Respirators: Use appropriate respirators when working with harmful chemicals or in poorly ventilated areas.
- Exhaust Ventilation: Install exhaust extraction systems to remove fumes from the workspace.
- Regular Checkups: Schedule periodic health checkups to monitor respiratory health.
7. Electrical Hazards
Mechanics often work with electrical systems in vehicles, which can pose risks of shock or burns.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Turn Off Power: Always disconnect the battery before working on a vehicle’s electrical system.
- Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to prevent electrical shock.
- Training: Ensure all workers are trained in basic electrical safety.
8. Mental and Physical Fatigue
Long hours, physical labor, and tight deadlines can lead to fatigue, increasing the risk of mistakes and injuries.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Adequate Rest: Take regular breaks to prevent overexertion and maintain focus.
- Work-Life Balance: Avoid excessive overtime and prioritize rest outside of work.
- Healthy Habits: Stay hydrated, eat nutritious meals, and engage in regular physical activity to maintain overall health.
9. Emergency Preparedness
Auto shops must be equipped to handle emergencies, such as fires, chemical spills, or injuries.
Health and Safety Tips:
- Emergency Training: Conduct regular drills to ensure all employees know what to do in case of an emergency.
- First Aid Kits: Maintain well-stocked first aid kits and ensure employees know how to use them.
- Emergency Exits: Clearly mark and keep emergency exits free of obstructions.
Conclusion
The diverse hazards faced by auto mechanics necessitate a strong focus on health and safety practices. By implementing measures such as proper ergonomics, chemical handling protocols, and emergency preparedness, mechanics can work more safely and efficiently. Employers must prioritize creating a safe environment, while mechanics should remain proactive about their own safety. Together, these efforts ensure a healthier, safer workplace for all.

No comments yet