Occupational health and safety (OH&S) management is critical for ensuring worker safety, minimizing risks, and improving overall business performance. Businesses around the world have utilized management standards like OHSAS 18001 to maintain high levels of workplace safety. However, a significant transition has been underway, with ISO 45001 replacing OHSAS 18001 as the new global standard for occupational health and safety management systems (OHSMS).
Organizations currently certified under OHSAS 18001 must migrate to ISO 45001 by the end of March 2021. Failure to transition will leave businesses without an accredited OHSMS, potentially risking non-compliance with health and safety regulations and forfeiting the benefits of certification.
In this article, we will delve into the key features of ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001, explore the differences between these two standards, and discuss why transitioning to ISO 45001 is crucial.
What Is ISO 45001?
ISO 45001 is an internationally recognized standard for occupational health and safety management systems. It is designed to provide a framework for organizations to proactively improve employee safety, reduce workplace risks, and create better working conditions.
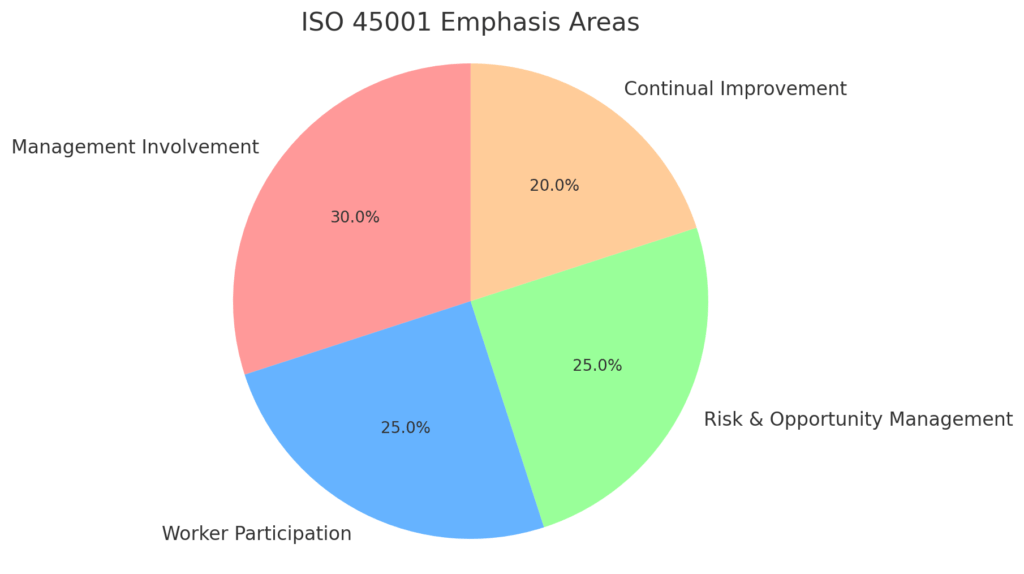
ISO 45001 emphasizes:
- Management commitment: Top management is actively involved in ensuring the health and safety of workers.
- Worker participation: Employees are involved in identifying risks and shaping safety procedures.
- Risk-based approach: Focuses on identifying and mitigating potential hazards before they cause harm.
This new standard, based on the High-Level Structure (Annex SL) framework shared with other ISO standards like ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), is designed to align seamlessly with an organization’s overall management processes. This integration makes it easier for businesses to implement ISO 45001 in conjunction with other management systems.
ISO 45001 is not simply a revision of OHSAS 18001—it is a completely new standard with a proactive approach to managing risks and opportunities, offering businesses a comprehensive and modern framework to manage occupational health and safety.
What Is OHSAS 18001?
OHSAS 18001 (Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series) was previously the widely recognized standard for occupational health and safety management systems. Introduced in 1999, it helped businesses identify, control, and reduce workplace hazards.
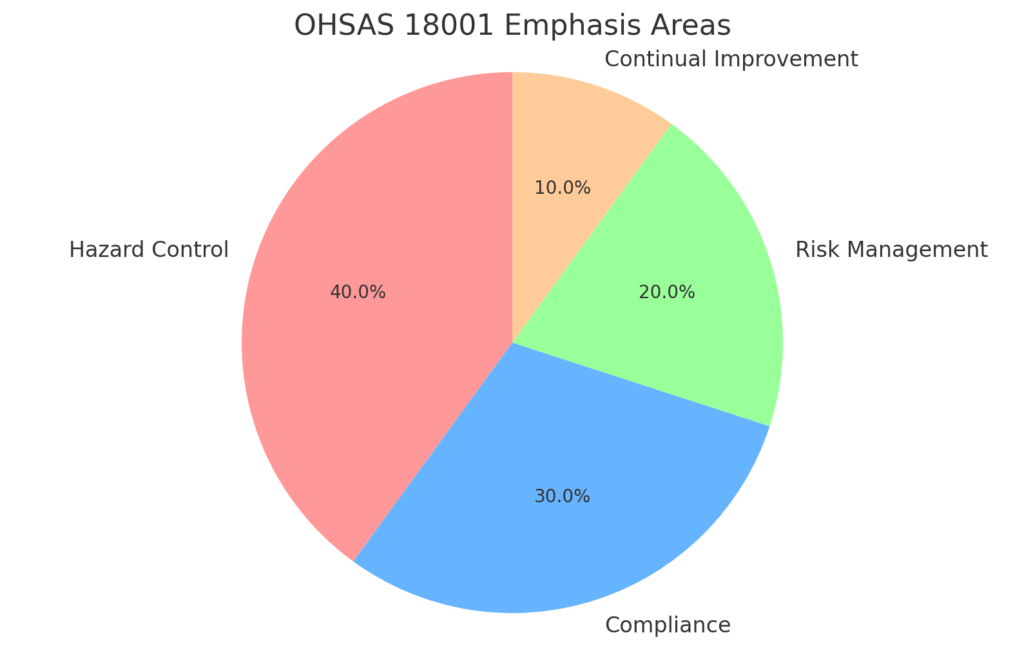
Key features of OHSAS 18001 include:
- Hazard control: Focused on managing workplace risks after they are identified.
- Legal compliance: Ensures compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
- Reactive approach: Risks are addressed once they manifest or are reported.
Although effective, OHSAS 18001 is considered reactive compared to the proactive approach of ISO 45001. As a result, the transition to ISO 45001 introduces new concepts that prioritize not only the prevention of hazards but also the identification of opportunities for improving safety.
Key Differences Between ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001
While both standards aim to ensure workplace safety and reduce risks, the differences between ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001 are substantial. Below are the key areas where these two standards diverge:
| Feature | OHSAS 18001 | ISO 45001 |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Reactive: Focuses on controlling hazards after identification. | Proactive: Evaluates and mitigates risks before they cause harm. |
| Structure | Based on the OHSAS framework, specific to occupational safety. | Based on Annex SL, aligning with other ISO standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. |
| Leadership & Commitment | Does not require top management involvement beyond basic compliance. | Requires active involvement of top management in health and safety systems. |
| Risk & Opportunity Management | Focuses solely on hazards and risks. | Considers both risks and opportunities to improve health and safety. |
| Worker Participation | Limited involvement of employees in the safety process. | Involves workers and other interested parties in identifying and mitigating risks. |
| Context of the Organization | Not a requirement to consider organizational context. | Requires consideration of internal and external factors that affect OH&S performance. |
| Continual Improvement | Improvement is focused on hazard elimination and compliance. | Requires a system for ongoing evaluation and improvement of the OH&S system. |
| Supply Chain Management | Does not require consideration of external suppliers and contractors. | Requires consideration of suppliers, contractors, and third parties in the OH&S system. |
In-Depth Comparisons
1. Proactive vs. Reactive Approach
The most notable difference between ISO 45001 and OHSAS 18001 is the shift from a reactive to a proactive approach. ISO 45001 encourages organizations to identify risks and opportunities for improvement before incidents occur. This shift enables businesses to create safer workplaces by addressing potential hazards early, reducing the likelihood of incidents.
2. Leadership & Management Commitment
ISO 45001 places a stronger emphasis on leadership and management commitment. Top management is required to take an active role in the health and safety system, ensuring that occupational health and safety are integrated into the overall management of the organization. This involvement is crucial for creating a culture of safety within the company.
3. Risk & Opportunity Management
ISO 45001 takes a more holistic view of risk management, considering not only the hazards but also opportunities to improve safety practices. This broadens the scope of occupational health and safety and encourages continuous improvement across the organization. OHSAS 18001, on the other hand, focuses primarily on hazard control without addressing opportunities for enhancement.
The Importance of Transitioning to ISO 45001
Organizations that fail to transition from OHSAS 18001 to ISO 45001 will be left without an accredited OH&S management system after March 2021. Beyond compliance, ISO 45001 offers several benefits:
- Improved workplace safety: By identifying and addressing risks early, businesses can drastically reduce workplace accidents and injuries.
- Enhanced worker participation: ISO 45001 fosters a collaborative environment where employees are actively involved in the health and safety process.
- Integrated management systems: The Annex SL framework makes it easier for businesses to align health and safety management with other key management systems like quality and environmental standards.
Businesses should begin their migration process early to ensure that they meet the deadline and reap the benefits of ISO 45001 certification.
ISO 45001 represents a major advancement in occupational health and safety management. With a stronger focus on leadership involvement, risk prevention, and continual improvement, this new standard sets a higher bar for businesses striving to maintain safe work environments.
As the transition deadline approaches, businesses must prioritize the migration process to avoid losing the benefits of certification and to ensure their health and safety practices are aligned with the latest industry standards.
By embracing ISO 45001, organizations will not only enhance workplace safety but also improve their overall operational efficiency, productivity, and compliance.

No comments yet